Why You Should Talk to a Bicycle Accident Lawyer After a Crash in San Antonio
Following a bicycle accident, it's important to get the medical and professional…
What People in Recovery Wish Others Understood About Addiction
Addiction is a topic that few people, outside of those who are…
AFM Disabler 5.3 Reviews: Which Product Is Worth Buying?
Introduction The relationship between the owners of Chevrolet and GM trucks with…
The Quiet After the Storm: Finding Footing When the Unthinkable Happens
Gainesville has a specific rhythm that everyone who lives here eventually falls…
The Snap, The Ache, and The Insurance Game
You are sitting at a red light. You are checking the radio…
The Quiet Chaos of a Western Mass Car Crash
You know the feeling. You’re cruising down the Mass Pike, maybe heading…
What Sets Professional Pest Control Methods Apart From Store-Bought Solutions in Orlando
Homes and businesses across Central Florida face constant pressure from insects, rodents,…
What Are the Most Common Types of Quick Loans
Short term borrowing options often attract attention during unexpected expenses or brief…
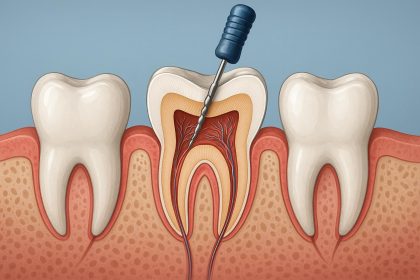
Signs A Dentist In North Austin May Suggest A Root Canal Treatment
A tooth can send clear messages when something deeper needs attention. Sensitivity,…
How to Develop Leaders for Crisis-Ready Communities
What happens when the power goes out, the streets flood and no…
Why Education Plays a Central Role in Social Responsibility
Have you ever wondered why people who’ve had more access to education…
Crypto Payments in Business: Why “Asset Mismatch” Is a Real Operational Risk
More companies are experimenting with crypto, not as a headline-grabbing bet, but…