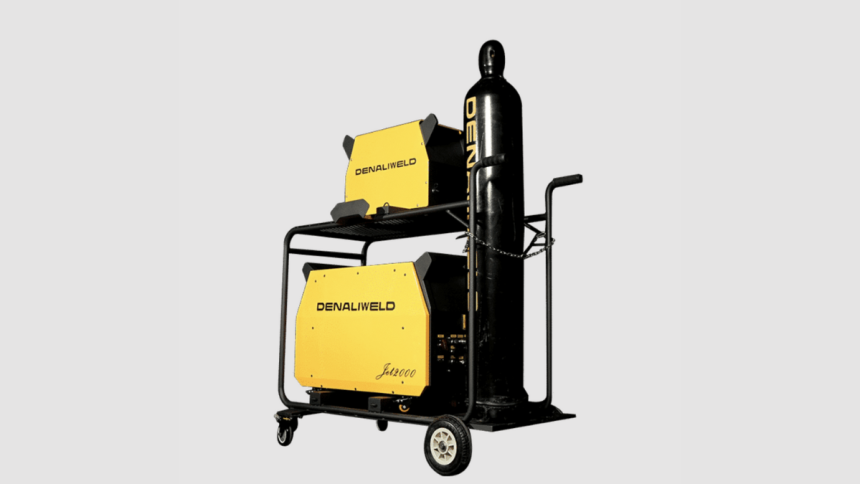
Revolutionary yet practical, handheld laser welding machines are transforming metalworking across industries. These compact devices deliver precision and efficiency that traditional welding methods simply can’t match. With their portable design and user-friendly interface, these tools are increasingly popular in workshops, manufacturing facilities, and repair shops.
In this article, you’ll discover how handheld laser welders work, their key advantages over conventional methods, and what to consider before investing in one. We’ll explore their applications across various industries, from automotive repair to jewelry making, and examine the features that distinguish top-performing models in today’s market.
Design & Portability
Handheld laser welders feature compact designs that transform precision welding into a mobile operation. Complete handheld laser welding units typically weigh 62-86 lbs (28-39 kg), with the actual welding head weighing approximately 2.2 lbs (≤1 kg), making extended operation manageable.
The ergonomic handles include intuitive controls positioned for one-handed operation. Touch screens and simple button interfaces allow quick parameter adjustments without interrupting workflow.
Modern units come with:
- Adjustable power settings (typically 500-3000 W)
- Interchangeable nozzles for different weld types
- Built-in cooling systems
Most systems require AC power with 220V connections, often three-phase, rather than battery power. This provides the consistent high power needed for industrial applications.
The fiber optic cable delivery system typically extends about 10 m (33 ft) from the power source, giving you flexibility to reach challenging weld locations. This setup distributes weight effectively, with the power unit resting on the floor while you maneuver just the lightweight welding head.
Because they require minimal setup area compared to traditional welding equipment, these systems can effectively accommodate crowded shops.
Performance & Efficiency
Handheld laser welders deliver exceptional performance metrics that translate directly to workplace productivity. These machines achieve welding speeds up to 3-4 times faster than traditional TIG welding methods while maintaining precision within 0.1 mm tolerance.
The weight distribution of modern handheld laser welders is practical – while power units weigh over 60 lbs (27 kg), the welding heads you handle are only about 2.2 lbs (1 kg). This design allows operators to complete precise welds with significantly less fatigue.
Energy consumption presents another advantage. Handheld laser welders use fiber technology that can consume approximately 40% less energy than YAG and arc welders. Most industrial units require 220V AC power rather than standard 110V circuits.
Heat affected zones (HAZ) are minimized to 0.5 mm or less with laser welding, resulting in:
- Reduced material distortion
- Stronger weld integrity
- Less post-weld finishing work
- Decreased material waste
The power density of handheld laser welders creates deep, narrow welds that outperform traditional methods in speed and quality. These machines focus energy precisely where needed, avoiding the surrounding material heating common with other welding approaches.
Maintenance requirements vary by manufacturer and usage intensity. Be sure to check the specific service schedule recommended for your equipment.
Control & Safety
User Interface
Handheld laser welders feature intuitive control panels with touch-screen displays or physical buttons that make operation straightforward. Most models include digital readouts showing real-time welding parameters such as power output, pulse frequency, and spot size. The interface allows quick adjustments between continuous, pulse, or spot welding modes without interrupting the workflow.
Safety Features
Laser welding requires comprehensive safety measures due to the Class 4 laser radiation involved. Modern handheld laser welders incorporate multiple safety systems:
- Embedded sensors that prevent firing unless proper contact with the workpiece is established
- Various additional safety features that may include auto-shutoff mechanisms, keycard activation, LED status indicators, and emergency stop buttons
Protective Equipment
Operating handheld laser welders demands proper protective gear in accordance with ANSI Z136.1 and IEC 60825-1 safety standards:
| Equipment | Protection Level | Standards Compliance |
| Laser safety glasses | OD 6+ at 1064-1080nm wavelength | ANSI Z136.1, EN 207 |
| Welding gloves | Heat resistant rating, EN 388 level 4 | ISO 11611, EN 407 |
| Protective clothing | Flame retardant rating | ISO 11611:2015 |
| Fume extraction systems | HEPA filtration | OSHA 29 CFR 1910.134 |
Training Requirements
Proper operation of handheld laser welders requires formal training. Manufacturers typically provide certification courses covering essential skills and safety protocols. For example, IPG Photonics offers an 8-hour “Laser Operator Safety & Basic Maintenance” course that includes:
- Laser fundamentals and safety principles (2 hours)
- Operational procedures and parameter selection (2 hours)
- Hands-on welding exercises (3 hours)
- Maintenance basics and troubleshooting (1 hour)
Training requirements vary by manufacturer and local regulations. Check with equipment suppliers for specific training recommendations and safety compliance requirements.
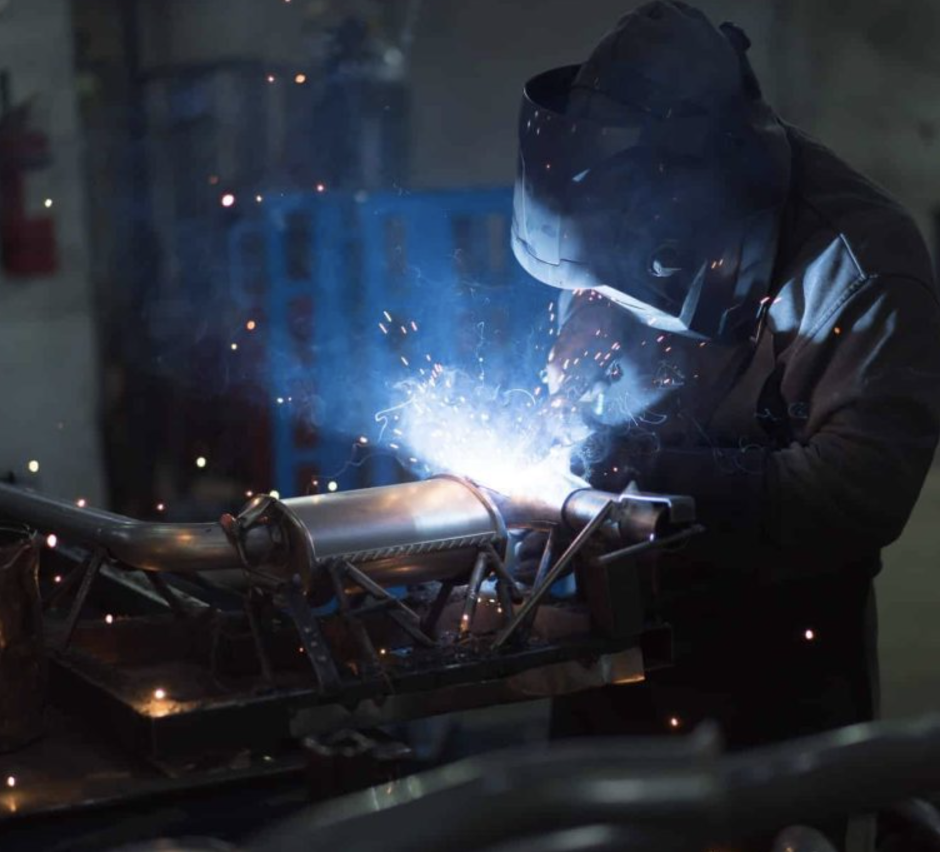

Welding Head & Material Handling
Handheld laser welders feature precision-engineered welding heads that maximize operational efficiency. The compact welding heads weigh approximately 2.2 lbs (≤1 kg) and connect to the main unit via a flexible fiber optic cable measuring around 10 m (33 ft) in length. This design allows you to access tight spaces and awkward angles that traditional welding equipment can’t reach.
Most modern welding heads include:
- Adjustable focal length settings
- Protective glass shields that prevent spatter contamination
- Quick-change nozzles for different application types
The ergonomic grip design reduces operator fatigue during extended welding sessions. Many manufacturers incorporate rubberized surfaces and balanced weight distribution to improve control during detailed work.
Material handling attachments complement the welding head capabilities. Wire feed systems integrate directly with the handheld unit, delivering filler material at rates typically between 38-600 mm/min (0.038-0.6 m/min). This automated feeding maintains consistent bead quality without requiring additional hands to manage the filler wire.
Advanced models feature integrated cooling systems that circulate water through the welding head, maintaining optimal operating temperatures even during continuous use. Water-chiller loops are standard on nearly all units to maintain laser performance.
Technical Specifications
Handheld laser welders come with varied technical specifications based on manufacturer and model. Here’s a breakdown of the critical parameters:
Power Output Range:
- Industrial handheld fiber lasers typically span 500-3000W
Laser Source Types:
- Fiber laser (most common)
- Nd:YAG (less common in handheld applications)
- CO₂ (rare in handheld applications)
Beam Properties:
- Spot size: 0.2-2.0 mm (adjustable)
- Wavelength: 1064-1080 nm (standard for fiber lasers)
- Beam quality factor (M²): 1.2-1.8
Material Compatibility:
- Stainless steel: up to 4 mm thickness
- Aluminum alloys: up to 2 mm thickness
- Copper: up to 1 mm thickness
- Titanium: up to 3 mm thickness
Operating Requirements:
- Power supply: 220V AC, often three-phase
- Water cooling systems (standard)
- Assist-gas pressures: 0.01-0.03 MPa (when required)
Physical Dimensions:
- Main unit dimensions approximately 1020×550×810 mm (40×22×32 in)
- Handpiece length: 12.7-20.3 cm (5-8 in)
- Fiber optic cable length: typically around 10 m (33 ft)
Industry Applications
Handheld laser welders serve diverse industrial applications:
- Aerospace: Used for titanium component repairs with high precision
- Automotive: Enables up to 4× faster aluminum joint welding compared to traditional methods
- Medical device: Provides clean, contamination-free welds for surgical instruments
- Jewelry: Creates nearly invisible seams on precious metals with minimal heat transfer
As with industrial equipment, specific performance metrics will vary by manufacturer and model. Request detailed specifications and demonstrations to verify capabilities when evaluating handheld laser welders for your application.
Denaliweld’s Innovation Engine & Global Impact
Denaliweld’s handheld laser welders incorporate an Innovation Engine that combines adaptive power modulation and real‑time sensor feedback to dynamically adjust welding parameters across diverse metals and thicknesses. This technology reduces trial‑and‑error setup, minimizes defects, and accelerates production workflows. Globally, Denaliweld systems are adopted in aerospace, automotive, and jewelry sectors, where consistent quality and rapid deployment drive both efficiency gains and broader application of precision laser welding.
Conclusion
Handheld laser welding machines are reshaping metal fabrication by combining speed, precision, and ease of use. With welding rates up to four times faster than TIG methods, tolerances within 0.1 mm, and minimal heat‑affected zones, these systems cut down on rework and material waste. Their compact, ergonomic designs reduce operator fatigue, while advanced features—like adaptive power modulation and real‑time feedback—ensure consistent, high‑quality results across a variety of metals and thicknesses. Whether you’re in automotive repair, aerospace, jewelry making, or general metalworking, a handheld laser welder offers a compelling blend of productivity and precision.
Have you considered how a handheld laser welder might transform your specific production challenges?”
Lynn Martelli is an editor at Readability. She received her MFA in Creative Writing from Antioch University and has worked as an editor for over 10 years. Lynn has edited a wide variety of books, including fiction, non-fiction, memoirs, and more. In her free time, Lynn enjoys reading, writing, and spending time with her family and friends.