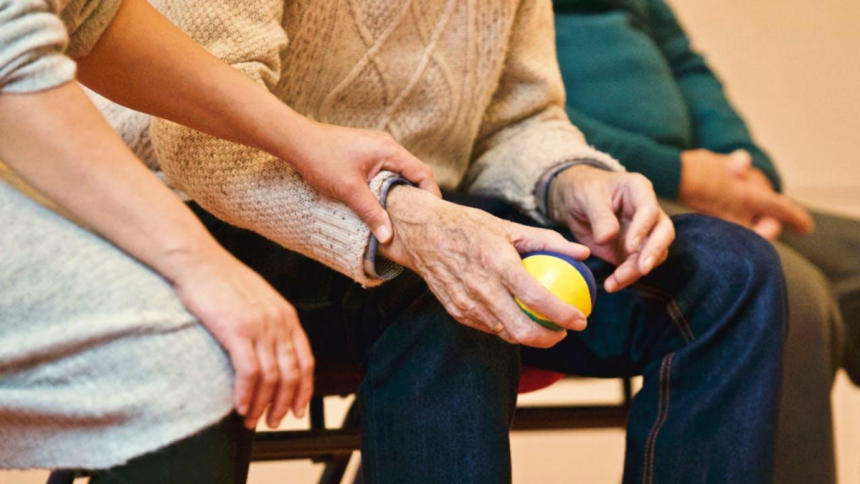
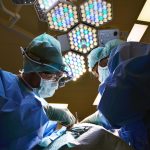
As the human body ages, it becomes more susceptible to various health issues, and the joints, being crucial to our mobility, are no exception. Elderly individuals often face a variety of joint problems that can significantly impact their quality of life. This article delves into some of the most prevalent joint issues encountered by the older population, providing insights into their causes, symptoms, and potential treatment avenues.
Finding the right medical support is crucial. Many turn to search for a clinic, which offers specialized care for these debilitating conditions.
Managing Joint Problems: Treatment Options and Considerations
As joint problems prevail among the elderly, finding effective treatments is vital. While some people look to manage their conditions through medication, physical therapy, or lifestyle changes, others might need more comprehensive care. When conservative treatments no longer provide relief, some elderly patients may consider surgery as an option to improve mobility and reduce pain.
Selecting a medical institution for joint surgery is a critical step that requires careful thought and research. For those seeking individualized attention and shorter wait times, one option to consider might be to find a private orthopedic surgery clinic in Montreal, where experienced professionals are equipped to offer advanced treatments tailored to each patient’s needs.
Osteoarthritis: The Degenerative Joint Disease
One of the most common joint ailments affecting seniors is osteoarthritis. This is a degenerative joint disease where the cartilage that cushions the ends of the bones wears down over time. Lack of cartilage leads to friction between bones, causing pain, swelling, and reduced motion in the joint. It can occur in any joint but most frequently affects knees, hips, hands, and the spine. As the condition progresses, individuals may notice a grinding sensation during movement and a decrease in joint flexibility. Treatment options focus on pain management and maintaining joint function, often including physical therapy and medication.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Autoimmune Condition
Rheumatoid arthritis is another serious concern for many elderly individuals. This autoimmune disorder does not only affect the joints but can also have systemic effects. It causes the immune system to mistakenly attack the lining of the joints, which leads to inflammation and can result in joint erosion and deformity over time. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to manage symptoms and prevent severe damage. Treatment strategies may involve immune-suppressing medications and lifestyle adjustments to alleviate pain and enhance quality of life.
Post-Traumatic Arthritis: Following Injury
Joints that have been injured through sports, accidents, or other trauma can develop what is known as post-traumatic arthritis. This condition can mimic the symptoms of osteoarthritis and may develop years after the initial injury. Chronic pain and stiffness are common complaints. Management of post-traumatic arthritis often includes methods to stabilize the joint, reduce load, and manage pain through both pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatments. Preventative measures and rehabilitation play a key role in managing the progression.
Gout: Metabolic Problems Causing Joint Pain
Gout is a type of arthritis characterized by sudden, severe attacks of pain, redness, and tenderness, often at the base of the big toe. It occurs when urate crystals accumulate around the joints because of elevated levels of uric acid in the blood, a condition often linked to dietary habits. It can be especially painful when not treated.
Bursitis: Inflammation of the Bursae
Bursitis is a painful condition that affects the small, fluid-filled sacs called bursae that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles near the joints. When bursae become inflamed, it results in pain and limited movement in the affected area. Commonly affected joints include the shoulder, elbow, and hip. Repetitive motion or prolonged pressure, often linked to specific activities or occupations, can trigger bursitis. Treatment typically involves rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medications to reduce pain and inflammation.
Tendinitis: Overuse and Aging Effects
Tendinitis is another joint-related condition that becomes more common with age. This condition involves the inflammation or irritation of a tendon, which are the thick fibrous cords that attach muscle to bone. It is often caused by repetitive movements or sudden injury, and it can cause significant pain and tenderness in the affected joint. Common sites for tendinitis include the shoulders, elbows, wrists, and heels. Managing tendinitis often involves rest, physical therapy, and medications to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. In severe cases, surgical intervention might be necessary to repair the damaged tendon.
Why Choose A Private Clinic for Orthopedic Surgery?
A private orthopedic clinic can provide various advantages, such as personalized service and expedited care. For complex joint issues, the expertise found in such facilities can make a significant difference in the outcomes of surgical procedures. Those opting for private care may also benefit from the state-of-the-art technology and innovative techniques employed by specialized surgeons.
Joint problems in the elderly are an unfortunately common part of aging. These conditions can hinder mobility and lessen the ability to lead an active, pain-free life. However, by understanding the symptoms and available treatments, seniors can better manage their conditions. If surgery becomes a necessary step, opting for a private surgery clinic could offer a more tailored and expedient path towards recovery. It is essential to engage healthcare providers in a thorough discussion to choose the best course of action for one’s unique situation, striving for revitalized joint health and enhanced overall wellbeing.
Lynn Martelli is an editor at Readability. She received her MFA in Creative Writing from Antioch University and has worked as an editor for over 10 years. Lynn has edited a wide variety of books, including fiction, non-fiction, memoirs, and more. In her free time, Lynn enjoys reading, writing, and spending time with her family and friends.