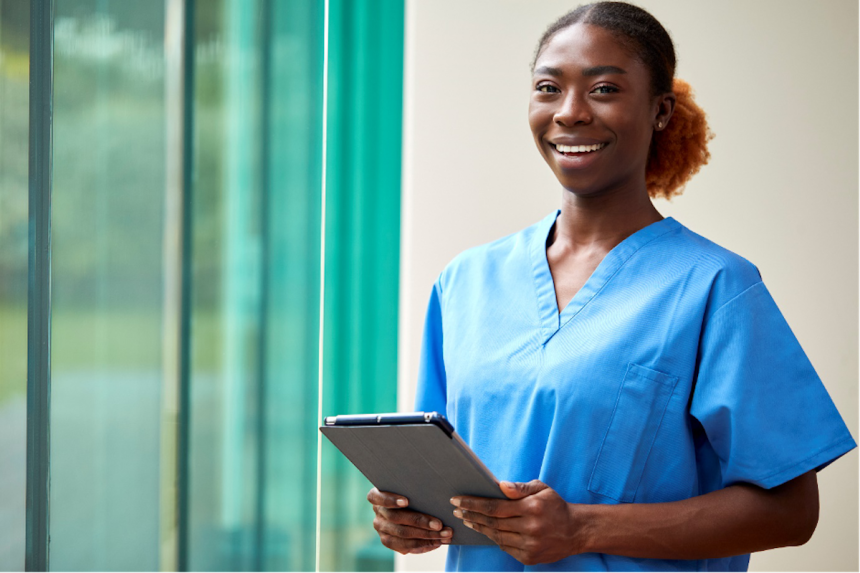
If you are not familiar with the term patient autonomy, a brief introduction is probably in order.
Patient autonomy refers to the principle that individuals have the right to make decisions about their own health and healthcare, free from coercion or undue influence.
This concept has become increasingly important in recent years as healthcare systems have shifted toward patient-centered care, which emphasizes the importance of respecting and valuing patients’ preferences and choices.
As healthcare professionals, nurses play a crucial role in promoting patient autonomy by educating and supporting patients as they make decisions about their care.
Understanding patient autonomy: definition and importance
Understanding patient autonomy is essential for healthcare professionals, especially nurses, as it is the foundation for patient-centered care.
The importance of patient autonomy is twofold.
Firstly, it promotes patients’ rights and respects their preferences, values and beliefs, which is a fundamental aspect of ethical care.
Secondly, it has been shown to lead to better health outcomes, as patients who are involved in decision-making are more likely to adhere to treatment regimens and have greater satisfaction with their care.
It’s important to note, however, that patient autonomy is not absolute and may be limited in certain situations.
For example, if a patient is unable to make decisions due to mental incapacity, healthcare professionals may have to make decisions on their behalf.
Additionally, in cases of emergencies, healthcare professionals may have to act quickly without the patient’s consent.
However, in these situations, healthcare professionals should strive to involve the patient or their family members as much as possible and, by doing so, they will be in a position to provide ethical, patient-centered care that leads to better health outcomes.
Nurses’ role in promoting patient autonomy
Promoting patient autonomy is a fundamental aspect of nursing practice.
We have already spoken about how nurses should empower patients to make informed decisions about their health and healthcare, but it goes much further than that.
Nurses are responsible for creating an environment that promotes autonomy, which includes ensuring that patients have access to the resources they need to make informed decisions and respecting patients’ right to refuse treatment.
They also have to ensure that patients are given enough time to make their decisions and to involve patients’ families and other healthcare team members in the decision-making process.
Promoting patient autonomy also requires nurses to continuously reflect on their own values and biases and how they might influence the care they provide.
This self-awareness is essential in maintaining objectivity and avoiding any form of coercion or undue influence when assisting patients in making decisions.
It should be mentioned for anyone who would like to truly embrace nursing autonomy that the online accelerated BSN programs offered by Baylor University are definitely worth further investigation.
The post-baccalaureate accelerated BSN program, for example, can be completed in one year, with 90% of nursing students receiving a job offer at the time of graduation.
Effective communication strategies for supporting patient decision-making
Effective communication is a vital component of promoting patient autonomy and supporting patient decision-making.
Nurses, as the primary caregivers, need to have good communication skills to be able to facilitate patient’s informed decision-making.
One key strategy is to use plain language and avoid medical jargon as much as possible.
This allows patients to understand the information being shared with them, which is essential in making informed decisions.
Another strategy is active listening, which involves fully paying attention to the patient, acknowledging and validating their concerns and clarifying any misunderstandings.
This helps the patient feel heard and valued, and it also helps the nurse to understand the patient’s perspective and preferences.
It is also important for nurses to explain the potential risks and benefits of different treatment options, along with the probability of success, therefore, allowing patients to weigh the pros and cons and make an informed decision.
Other healthcare team members should also be involved in the decision-making process because this can be extremely beneficial as family members may have a different perspective and can provide additional support for the patient.
The patient’s decision-making capacity and respecting the patient’s right to make decisions should also be considered.
For example, if a patient is not capable of making their own decisions, the nurse should involve the patient’s legal guardian or next of kin and act in the patient’s best interest.
Implementing patient autonomy in practice: best practices and challenges
Implementing patient autonomy in practice is essential for providing patient-centered care, but it can also present several challenges, so let’s explore some best practices and challenges associated with implementing patient autonomy in healthcare practice.
Best practices:
- Provide patients with accurate and relevant information, allowing them to make informed decisions about their health and healthcare
- Respect patient values, beliefs and cultural backgrounds
- Involve patients and their families in the decision-making process
- Create an environment that promotes autonomy
- Continuously reflect on own values and biases and how they may influence care
- Assess patient decision-making capacity and respect patient’s right to make decisions
Challenges:
- Limited patient understanding or ability to make decisions
- Time constraints and competing priorities in practice
- Communication barriers, such as language and literacy challenges
- Patient’s emotional state, such as depression or anxiety, can affect their ability to make decisions
- Resistance from patients, families or other healthcare team members
- Legal and ethical considerations, such as issues related to consent or end-of-life care
It’s important to note that these challenges are not insurmountable, and they can be managed with the right approach and strategies.
For example, utilizing community resources and language-interpreting services can help overcome language and literacy challenges.
Collaborating with other healthcare team members can also help in identifying and addressing emotional or psychological challenges that might be affecting the patient’s decision-making ability.
Additionally, providing education to patients, families and other healthcare team members on the importance of patient autonomy can help to increase support and understanding of the concept.
To sum up, implementing patient autonomy in practice requires a dedicated effort from healthcare professionals, but by following best practices and addressing the challenges, nurses can support patients to make informed decisions about their healthcare and promote autonomy in practice.
Lynn Martelli is an editor at Readability. She received her MFA in Creative Writing from Antioch University and has worked as an editor for over 10 years. Lynn has edited a wide variety of books, including fiction, non-fiction, memoirs, and more. In her free time, Lynn enjoys reading, writing, and spending time with her family and friends.