Introduction
In today’s competitive industrial landscape, gear transmission systems are critical components across sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery. However, manufacturers often face persistent challenges, including inefficiency, excessive noise, premature wear, and unplanned downtime due to traditional gear machining methods failing to meet high-precision demands. These issues lead to cost overruns and project delays, rooted in improper gear type selection, imprecise manufacturing processes, lack of sustainable practices, and reliance on outdated technologies that fall short of smart manufacturing trends.
This article provides a comprehensive guide based on precision gear machining, offering actionable strategies to avoid common errors. By following this guide, manufacturers will master key approaches to ensure reliability in gear-driven systems, transitioning smoothly into the detailed strategies below.
What Are the Fundamental Types of Gears and Their Industrial Applications?
Gears are the backbone of mechanical systems, and selecting the right type is crucial for optimal performance. Missteps in this area can result in significant efficiency losses and operational failures.
1. Overview of Common Gear Types and Their Characteristics
The most prevalent gear types include spur gears, helical gears, bevel gears, and worm gears. Each has distinct structural features and applications:
- Spur gears: are simple and cost-effective, ideal for parallel shaft transmissions in applications like conveyor systems, but they can generate noise at high speeds.
- Helical gears: feature angled teeth that engage gradually, reducing noise and vibration, making them suitable for automotive transmissions where quiet operation is essential.
- Bevel gears: are used for intersecting shafts, commonly in differential drives, while worm gears offer high reduction ratios in compact spaces, such as lifting equipment.
Understanding these basics helps prevent mismatches that lead to wear or failure.
2. Industrial Case Studies and Selection Guidelines
Real-world examples highlight the importance of correct selection. For instance, in automotive applications, helical gears are preferred over spur gears to minimize noise and improve longevity. Conversely, using spur gears in high-torque scenarios without proper hardening can cause premature failure.
Comprehensive analysis on gear types, including detailed classifications and applications, is readily available in dedicated technical guides.For example, The Ultimate Guide to Gear Types provides a more in-depth classification analysis and practical application scenarios.Additionally, adherence to standards like ASME Y14.5 ensures gear tooth profile accuracy, avoiding misapplication errors by defining tolerance controls that influence type selection.
3. Consequences of Improper Gear Type Choice
Choosing the wrong gear type can lead to cascading issues, such as increased energy consumption, noise pollution, and reduced system lifespan. For example, in industrial machinery, incorrect bevel gear alignment may result in shaft misalignment, escalating maintenance costs by up to 30%. By aligning gear selection with functional requirements, manufacturers can enhance system reliability and avoid these pitfalls.
How Does Precision Gear Machining Enhance Manufacturing Efficiency and Reduce Costs?
Precision gear machining leverages advanced technologies like CNC milling and hobbing to achieve tolerances that traditional methods cannot match, directly impacting efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- The Role of CNC Technology in Gear Quality Improvement: CNC machining enables high-precision gear production by automating processes, reducing human error, and ensuring consistency. For example, by minimizing surface imperfections, precision machining can increase gear efficiency from 90% to 98%, lowering friction and energy loss. This translates to long-term savings, as demonstrated by a 20% reduction in maintenance costs over five years compared to conventional methods.
Firms with certifications like ISO 9001 uphold rigorous quality systems, ensuring machining consistency that minimizes errors and optimizes costs.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis of Precision vs. Traditional Machining: A comparative analysis shows that while precision machining may have higher upfront costs, it offers superior return on investment. Traditional methods often incur hidden expenses from rework and downtime, whereas precision techniques reduce scrap rates and enhance throughput. Data indicates that manufacturers adopting precision gear machining can achieve per-part cost savings of up to 25% through improved tool life and faster cycle times.
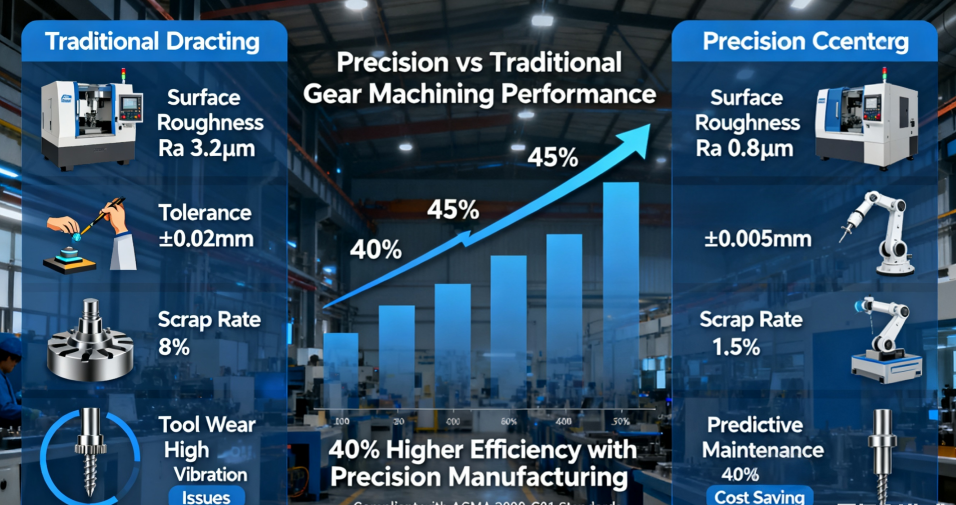
- Long-Term Efficiency Gains: Beyond immediate cost reductions, precision machining supports scalability and adaptability. For instance, the ability to produce gears with tighter tolerances ensures compatibility in high-stakes applications like wind turbines, where reliability is paramount. This strategic approach aligns with ISO 9001 frameworks, emphasizing continuous improvement and sustainable efficiency.
What Are the Most Common Challenges in Gear Manufacturing and How Can They Be Overcome?
Gear manufacturing is fraught with challenges, but proactive strategies can mitigate risks and enhance outcomes.
1. Identifying Key Challenges: Wear, Misalignment, and Thermal Deformation
Common issues include tooth surface wear due to inadequate lubrication, alignment errors from fixturing inaccuracies, and thermal deformation during heat treatment. These can lead to system failures, as seen in aerospace applications where gear misalignment caused by tolerances beyond ASME Y14.5 standards resulted in costly recalls.
2. Solutions Through Advanced Processes and Technologies
Implementing heat treatment techniques like carburizing can enhance surface hardness and durability, while 5-axis CNC machining ensures precise alignment by handling complex geometries in a single setup. For example, an aviation project resolved gear noise issues by adopting multi-axis CNC, reducing downtime by 40%.
Regular reference to standards like ASME Y14.5 helps manufacturers manage tolerances scientifically, overcoming alignment challenges through controlled processes.
3. Case Example: Overcoming Noise and Vibration
In one industrial case, a manufacturer faced excessive vibration from helical gears; by optimizing tooth profile precision using CNC grinding, they achieved a 15% improvement in smooth operation, highlighting how technical refinements address root causes.
How Can Sustainable Manufacturing Practices Be Integrated into Gear Production?
Sustainability is no longer optional; it drives efficiency and cost savings in gear production by reducing waste and enhancing brand reputation.
- Adopting Eco-Friendly Materials and Processes: Using recyclable materials like certified alloys and optimizing cutting fluid recycling systems minimize environmental impact. For instance, implementing closed-loop coolant systems can reduce fluid consumption by 50%, lowering disposal costs and aligning with EPA guidelines for environmental compliance.
These practices not only cut waste but also improve operational efficiency, as lean manufacturing principles reduce energy use by up to 10%.
- Economic Benefits of Sustainable Integration: Sustainable practices lead to tangible cost reductions, such as lower regulatory compliance expenses and enhanced market access. Data shows that companies focusing on sustainability report long-term savings of 10-15% through improved resource efficiency and customer preference for eco-conscious partners.
- Aligning with Global Standards: Referencing frameworks like ISO 14001 for environmental management ensures that gear production meets international benchmarks, reducing risks and fostering innovation in sustainable gear production.
What Role Does Smart Manufacturing Play in Modern Gear Machining?
Smart manufacturing, powered by Industry 4.0 technologies, revolutionizes gear machining by enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance.
1. IoT and AI Applications for Predictive Maintenance
IoT sensors embedded in CNC machines collect data on tool wear and performance, allowing AI algorithms to predict failures before they occur. For example, in automotive gear production, smart systems can forecast maintenance needs, reducing unplanned downtime by 30% and enhancing product quality.
Resources from organizations like NIST provide guidelines on smart manufacturing, bolstering credibility for these technologies.
2. Enhancing Precision with Digital Twins and Automation
Digital twins simulate gear behavior under various conditions, optimizing designs pre-production. This reduces prototyping costs and accelerates time-to-market, while automation ensures consistency in high-volume runs, crucial for applications requiring precision gear machining.
3. Real-World Impact on Efficiency
A case study in heavy machinery showed that integrating smart sensors improved gear quality by 25%, demonstrating how these technologies transform traditional processes into agile, data-driven operations.
How to Choose the Right Gear Machining Service for Specific Project Needs?
Selecting an appropriate machining service is critical for project success, requiring evaluation of multiple factors beyond price.
1. Key Selection Criteria: Precision, Materials, and Lead Times
Factors include accuracy levels (e.g., AGMA standards), material options like steel or aluminum, and delivery timelines. For custom needs, specialized suppliers offering online gear machining solutions provide the necessary flexibility to accommodate complex project requirements.
Certifications such as ISO 9001 and AS9100D (for aerospace) indicate a supplier’s commitment to quality, reducing risks in critical applications.
2. The Importance of Customization and Technical Support
A collaborative partner offers DFM (Design for Manufacturability) feedback early in the design phase, avoiding costly errors. The table below summarizes the collaboration phases and benefits:
| Collaboration Phase | Core Action | Expected Benefit |
| Concept Design | Early DFM consultation with supplier engineers | Avoid fundamental design flaws, lock in majority of costs |
| Detailed Design | Joint tolerance optimization and material selection | Enhance performance while reducing waste |
| Prototype Validation | Rapid prototyping for form and function testing | Minimize risks before mass production |
| Production & Quality | Rigorous inspection using CMM and other tools | Ensure consistent quality and compliance |
Table 1: illustrates the entire process of collaboration from conceptual design to production quality, demonstrating how early intervention and continuous validation effectively manage risks, optimize costs, and ensure the quality of the final output.
3. Making an Informed Decision
By prioritizing technical capabilities over low quotes, manufacturers can achieve lower total cost of ownership. For specialized requirements, exploring online gear machining services that offer end-to-end support ensures project alignment with industry standards.
Conclusion
Precision gear machining is a strategic imperative for avoiding costly errors in industrial applications. By correctly selecting gear types, adopting advanced machining techniques, integrating sustainable practices, and leveraging smart technologies, manufacturers can significantly enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure system reliability. This guide provides a roadmap for implementing these strategies, emphasizing collaboration with qualified partners to achieve long-term success.
FAQs
Q1: What is the typical lead time for custom gear machining?
A: Lead times vary based on complexity, but precision services often deliver prototypes in 5-15 days. Factors like material and heat treatment can affect this, and providers optimize schedules for efficiency.
Q2: How does gear type selection impact overall system efficiency?
A: Selecting the appropriate gear type — such as opting for helical instead of spur gears in high-speed applications — directly influences noise levels, vibration, and meshing efficiency. Properly chosen gears operate more smoothly, reduce energy loss through optimized tooth engagement, and can achieve transmission efficiencies of up to 98%, as outlined in industry technical guides.
Q3: Can sustainable practices reduce gear machining costs?
A: Yes, integrating sustainable manufacturing practices — including coolant recycling systems and the use of energy-efficient CNC machinery — not only supports environmental compliance but also significantly lowers operational waste and energy consumption. Many manufacturers report long-term cost savings of 10–15% due to reduced resource use and lower disposal fees.
Q4: What certifications should I look for in a gear machining provider?
A: It is essential to prioritize suppliers with ISO 9001 certification for consistent quality management and AS9100D certification if components are intended for aerospace applications. These credentials validate that the provider follows internationally recognized standards, effectively reducing risks in critical or highly regulated projects.
Q5: How do smart manufacturing technologies improve gear quality?
A: Through the integration of IoT sensors and AI-driven analytics, smart systems enable real-time monitoring of machining conditions and predictive maintenance alerts. This approach minimizes unexpected tool wear or machine deviations, leading to higher gear precision, fewer defects, and less unplanned downtime.
Author Bio
The author is a precision manufacturing expert at LS Manufacturing, a company specializing in high-quality gear solutions, holds certifications such as ISO 9001 and IATF 16949, dedicated to helping clients overcome challenges in industrial applications. For a custom gear machining quote or to learn more, visit their online gear machining services page or contact their experts for project consultations.
Lynn Martelli is an editor at Readability. She received her MFA in Creative Writing from Antioch University and has worked as an editor for over 10 years. Lynn has edited a wide variety of books, including fiction, non-fiction, memoirs, and more. In her free time, Lynn enjoys reading, writing, and spending time with her family and friends.















