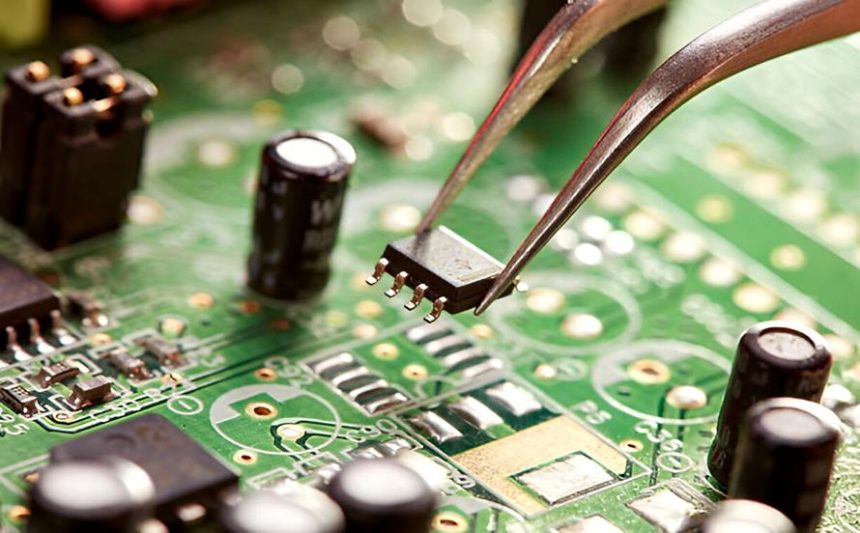
Control board assembly is the process of designing, fabricating, and assembling printed circuit boards (PCBs) that serve as the brain of countless electronic devices. These boards manage the flow of signals and power, enabling machines, appliances, and systems to function seamlessly. From home appliances and industrial machinery to medical devices and automotive electronics, control board assembly plays a crucial role in ensuring operational efficiency and reliability.
The process involves careful placement of electronic components, precise soldering, and thorough testing to make sure the control board performs as intended. Given the complexity of modern electronics, control boards often require advanced assembly techniques, such as surface-mount technology (SMT), through-hole soldering, and automated inspection.
Importance of Control Board Assembly in Modern Electronics
Control boards are vital for the smooth operation of nearly every electronic device. They act as the central hub, coordinating inputs, outputs, and power distribution. A well-assembled control board ensures that the device not only functions correctly but also maintains high levels of safety and durability.
In consumer electronics, control boards regulate functions such as timing, temperature, and user inputs. In industrial systems, they monitor performance, reduce downtime, and enhance efficiency. The importance of control board assembly cannot be overstated, as even a minor error in assembly can lead to costly failures, product recalls, or safety hazards.
The Process of Control Board Assembly
The assembly of a control board typically follows several structured stages:
- Design and Layout Preparation – Engineers create detailed schematics and PCB layouts that determine how the board will function and where each component will be placed.
- Component Procurement – Depending on the project, components are either sourced by the assembler or provided by the customer.
- PCB Fabrication – The bare board is manufactured, with copper traces, vias, and layers that establish the electrical pathways.
- Component Placement – Automated pick-and-place machines position components onto the board with exceptional speed and accuracy.
- Soldering – Components are soldered using reflow ovens for SMT parts and wave soldering or manual soldering for through-hole parts.
- Inspection and Testing – Automated Optical Inspection (AOI), X-ray inspection, and functional testing are conducted to ensure quality and performance.
- Final Assembly – The control board may be integrated into housings or tested within the larger system to confirm reliability.
Challenges in Control Board Assembly
Despite advancements in technology, control board assembly presents several challenges. Miniaturization of electronics demands precise component placement and soldering of fine-pitch devices. Heat management also becomes a concern as boards must handle increasing power densities without compromising performance.
Supply chain disruptions can affect the availability of components, delaying assembly schedules. Additionally, maintaining consistent quality across large production runs requires strict process controls and adherence to international standards such as IPC-A-610.
Manufacturers must also balance cost efficiency with reliability. Using low-quality components or skipping essential testing steps can reduce upfront expenses but lead to long-term problems. This makes choosing an experienced assembly partner critical to success.
Applications of Control Board Assembly
Control board assembly finds applications in a wide range of industries. In the automotive sector, control boards manage engine systems, infotainment, and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). In healthcare, they are essential for diagnostic machines, patient monitoring devices, and life-saving equipment.
Home appliances such as washing machines, refrigerators, and air conditioners also rely heavily on control boards to provide automated functionality and user convenience. In industrial automation, control boards are used in robotics, conveyor systems, and power management equipment.
The versatility of control board assembly demonstrates its significance in enabling smarter, safer, and more efficient technologies across all sectors.
Why Quality Matters in Control Board Assembly
The performance of an entire device often depends on the quality of its control board. Poorly assembled boards can lead to inconsistent performance, safety risks, or product failures. High-quality control board assembly ensures signal integrity, reduces electromagnetic interference, and extends product lifespan.
Furthermore, adherence to strict testing protocols ensures that boards meet industry-specific regulations, which is especially critical in medical, aerospace, and defense applications. For companies developing advanced electronics, investing in reliable assembly is not just a technical requirement but also a strategic business decision.
Conclusion
Control board assembly is the foundation of modern electronics, providing the functionality and intelligence behind everyday devices and complex industrial systems. Its importance spans across industries, ensuring efficiency, reliability, and innovation in technology. By focusing on precision, quality assurance, and advanced assembly techniques, businesses can achieve long-lasting and dependable products.
If your organization is seeking the best PCB assembly service to handle complex control board assembly projects, partnering with a trusted provider can ensure your products meet the highest standards of performance and reliability.
Lynn Martelli is an editor at Readability. She received her MFA in Creative Writing from Antioch University and has worked as an editor for over 10 years. Lynn has edited a wide variety of books, including fiction, non-fiction, memoirs, and more. In her free time, Lynn enjoys reading, writing, and spending time with her family and friends.